Vocabulary
The student will build a working vocabulary of common שרשים, שמות עצם, and other frequently used words in the חומש.
| Enduring Understandings |
|---|
| 1. Any translation of לשון הקודש is already interpretive, and therefore the full meaning of the תורה can only be accessed in its original language. |
| 2. No two languages are identical, and therefore many words in לשון הקודש will not have one exact translation in English which conveys its full, multifaceted meaning. |
| 3. A student must know 90% of words in a text to be able to independently study that text. [Knowledge of less than 75% of the words in the text is “frustration level – un-teachable.”] [10] |
| 4. In לשון הקדוש, the שורש or שם עצם is the foundation of almost every word in חומש, and learning a large number of these roots and basic words gives us access to most of the words that will appear in all of חומש.i[11] |
| 5. Words in לשון הקדוש are interrelated, so learning vocabulary words gives a student access to a much greater number of as of yet unfamiliar but related words. |
| Essential Questions |
|---|
| 1. Why do I need to learn לשון הקדש? |
| 2. What is the best way to translate this word in this context? |
| 3. Is it important to know every single word in a given text before approaching it? |
| 4. What is the שורש/שם עצם of this word? |
| 5. How is this word related or similar to a word that you have already learned? |
[10] Gunning, 1998. Assessing and correcting reading and writing difficulty.
[11] See the Appendix to this standard for relevant studies and word lists.
Key Knowledge:
- There are many rules in לשון הקודש and for every rule, there are always exceptions
- A noun in Hebrew is called a שם עצם. The word שם עצם refers to the singular version of that noun, and is considered the base word for all related forms of that noun. (E.g. משפחה is the שם עצם. Related forms include משפחות, למפשחותיהם, משפחתי, etc.)
- A שורש refers to the root of a verb. It is comprised of 3 letters that should be presented with periods/full stops between each letter, and cannot be pronounced.
- When a שורש appears in the word, sometimes the 3 letters do not appear consecutively, or, some of the letters of the שורש may not appear in the word at all.
- A verb in Hebrew is called a פועל. Every פועל has a שורש as its root. When a שורש is conjugated into various forms (בנינים, tense, etc. – see Verbs in Parts of Speech below), and given נקודות, it becomes a פועל (which can then be pronounced).
- When referring to the letters of a שורש ,the first letter is called the פ הפועל’ the second letter of the שורש is referred to as the ‘ע הפועל and the last letter is referred to as the ל הפועל’ .These are often abbreviated to פה”פ, עה”פ, לה”פ.
- There are unique שורשים that are considered “weak שורשים” and they often lose letters or have different ניקוד than other שורשים in the same בנין .We refer to these unique שורשים by their weak letter. For example שורשים that are in the category of ע”ו mean שורשים where the ע’ הפועל is the letter ו’ such as ק.ו.מ. Other categories include: פ”נ, פ”י, פ”א, ע”י, ל”ה, ל”א.
- Some words, depending on how they are used, can function as nouns, verbs, or adjectives. (E.g. קטן can be both a noun and adjective, and can be conjugated as a verb such as קטונתי. The word שופט is a noun, adjective and verb.)
- In these standards, all words are divided into three categories: nouns, shorashim for verbs and “other words”. These other words include numbers, pronouns, prepositions and conjunctions.
Note to Teachers: Explicit, direct instruction strategies for vocabulary include the introduction of new words, including definitions, and the use of concrete examples whenever possible. Students should be given the opportunity to use the words in context rather than in isolation. Oral vocabulary activities and games can make vocabulary learning a more enjoyable experience.
3.01 Vocabulary: שמות עצם (nouns)
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
E. States multiple translations of a single word, when those translations have been learned in the פסוקים. (i.e. רוח – wind, spirit).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
E. States multiple translations of a single word, when those translations have been learned in the פסוקים. (i.e. רוח – wind, spirit).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
E. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, ראש, רוח).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
E. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, ראש, רוח).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק.
E. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, ראש, רוח).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק.
E. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוקi(כי, ראש, רוח).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק.
E. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוקi(כי, ראש, רוח).
B. Provides the correct שם עצם from A when given its English translation.
C. Identifies and groups nouns in the חומש that share the same שם עצם, learned in A.
D. Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק.
E. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוקi(כי, ראש, רוח).
Grade 2: States the meaning of 25 new and 25 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 50.
Grade 3: States the meaning of 25 new and 50 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 75.
Grade 4: States the meaning of 25 new and 75 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 100.
Grade 5: States the meaning of 25 new and 100 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 125.
Grade 6: States the meaning of 25 new and 125 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 150.
Grade 7: States the meaning of 25 new and 150 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 175.
Grade 8: States the meaning of 25 new and 175 previously learned שמות עצם, equaling a total of 200.
Grades 5-8: Identifies and translates previously learned שמות עצם in an unlearned פסוק.
Grades 3-5: For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, ראש, רוח).
Grades 6-8: For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוק. (כי, ראש, רוח).
Resources
Supplements: Sample Nouns Per Grade
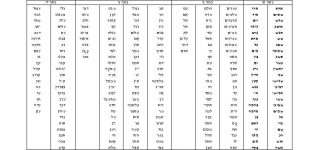
A suggested list of שמות עצם and other מילים to be mastered in each grade level.
Supplements: Vocabulary
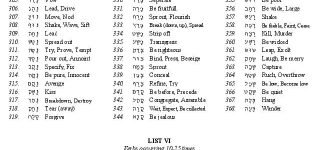
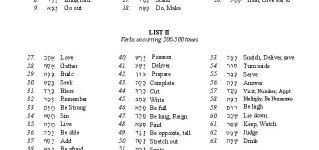
A list of vocabulary words appearing in order of their frequency in the חומש.
3.02 Vocabulary: שורשים (for verbs)
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, when all three letters of the שורש appear consecutively in the word, from שורשים learned in A.
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. N/A
F. N/A
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, when all three letters of the שורש appear consecutively in the word, from שורשים learned in A.
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. N/A
F. N/A
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies the 4 letters which are commonly left out (יונה)i[12] and identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, when two or three letters of the שורש appear consecutively in the word.
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
F. States multiple translations of a single שורש, when those translations have been learned in the פסוקים.i[15]
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies the 4 letters which are commonly left out (יונה)i[12] and identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, when two or three letters of the שורש appear consecutively in the word.
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
F. States multiple translations of a single שורש, when those translations have been learned in the פסוקים.i[15]
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies the 4 letters which are commonly left out (יונה), and identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, including the following variations: 3 letters with a י between them (ממליך), 2 letters with a י between them (הגיד), and when the first letter of the שורש is a י and is replaced by a וi(הוליד, הוסיף, הוריד).i[13]
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
F. For שורשים with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. [16]
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies the 4 letters which are commonly left out (יונה), and identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, including the following variations: 3 letters with a י between them (ממליך), 2 letters with a י between them (הגיד), and when the first letter of the שורש is a י and is replaced by a וi(הוליד, הוסיף, הוריד).i[13]
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק.
F. For שורשים with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. [16]
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies all שרשים in learned חומש, including both שלמים and חסרים.
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק.
F. For שורשים with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוק.
B. Provides the correct שורש from A when given its meaning in English.
C. Identifies all שרשים in learned חומש, including both שלמים and חסרים.
D. Identifies and groups verbs (and adjectives[14]) in the חומש that share the same שורש, from שורשים learned in A.
E. Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק.
F. For שורשים with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוק.
Grade 2: States the meaning of 25 new and 15 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 40.
Grade 3: States the meaning of 25 new and 40 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 65.
Grade 4: States the meaning of 25 new and 65 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 90.
Grade 5: States the meaning of 25 new and 90 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 115.
Grade 6: States the meaning of 25 new and 115 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 140.
Grade 7: States the meaning of 25 new and 140 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 165.
Grade 8: States the meaning of 25 new and 165 previously learned שורשים, equaling a total of 190.
Grades 3-4: Identifies the 4 letters which are commonly left out (יונה)i[12] and identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, when two or three letters of the שורש appear consecutively in the word.
Grades 5-6: Identifies the 4 letters which are commonly left out (יונה), and identifies the שורש in the חומש, from שורשים learned in A, including the following variations: 3 letters with a י between them (ממליך),i2 letters with a י between them (הגיד), and when the first letter of the שורש is a י and is replaced by a וi(הוליד, הוסיף, הוריד)i[13]
Grades 7-8: Identifies all שרשים in learned חומש, including both שלמים and חסרים.
Grades 3-5: Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק when prompted by the teacher.
Grades 6-8: Identifies and translates previously learned שורשים in an unlearned פסוק.
Grades 3-4: States multiple translations of a single שורש, when those translations have been learned in the פסוקים.i[15]
Grades 5-6: For שורשים with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. [16]
Grades 7-8: For שורשים with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוק.
[12] These 4 letters are indicated by the mnemonic יונה פרח. A fifth letter, ל, is dropped only from the שרש, לקח.
[13] These variations should be taught when they appear in the text being learned.
[14] Verbs and adjectives are grouped together here, because they often function in similar ways. Adjectives are conjugated in the same way as verbs in הווה, in בנין קל. (E.g גדול, גדולה, גדולים, גדולות.)
[15] E.g. the word וירא in בראשית י“ח, ב
[16] For example, רש“י on ויגדל – שמות, פרק ב, פסוק י’,י”א.
Resources
Supplements: Sample Nouns Per Grade
A suggested list of שמות עצם and other מילים to be mastered in each grade level.
Supplements: Vocabulary
A list of vocabulary words appearing in order of their frequency in the חומש.
3.03 Other Vocabulary
Prepositions and conjunctions (connecting words)[17] and other vocabulary (adverbs, numbers, questioning words, etc.)[18]
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
C. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, את, עוד, על)
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
C. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, את, עוד, על)
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
C. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, את, עוד, על)
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
C. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוקII (כי, את, עוד, על)
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
C. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוקII (כי, את, עוד, על)
B. Provides the correct Hebrew word from A when given its English translation.
C. For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוקII (כי, את, עוד, על)
Grade 2: States the meaning of 25 new and 25 previously learned words, equaling a total of 50.
Grade 3: States the meaning of 25 new and 50 previously learned words, equaling a total of 75.
Grade 4: States the meaning of 25 new and 75 previously learned words, equaling a total of 100.
Grade 5: States the meaning of 25 new and 100 previously learned words, equaling a total of 125.
Grade 6: States the meaning of 25 new and 125 previously learned words, equaling a total of 150.
Grade 7: States the meaning of 25 new and 150 previously learned words, equaling a total of 175.
Grade 8: States the meaning of 25 new and 175 previously learned words, equaling a total of 200.
Grades 3-6: For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, when the rest of the פסוק has been taught. (כי, את, עוד,על)
Grades 6-8: For words with multiple translations, can choose the appropriate translation for a given word based on its context, in an unlearned פסוק II (כי, את, עוד,על)